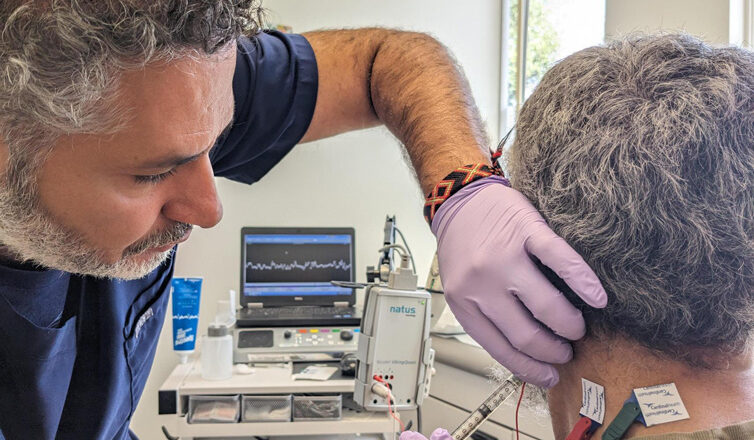
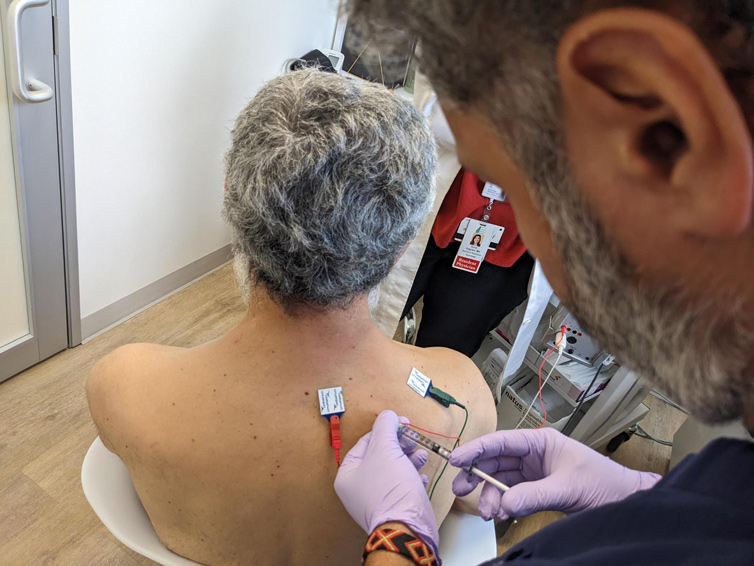
Botulinum toxin therapy is often the first line of treatment for some neurological conditions. The drug is made from a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. The injections weaken or paralyze certain muscles or block certain nerve signals, often reducing muscle spasms and pain. Our neurologists at Austin Neuromuscular Center use the botulinum toxin in very small amounts, but the injections can make a big impact on the patient’s quality of life.
“We do the injections under electromyography (EMG) or ultrasound guidance, and the effects can last around three months,” said neurologist Dr. Yessar Hussain. “For some patients, botulinum toxin treatment can make a big difference with disease management which could impact their activity in daily living.”
Who May Benefit from Botulinum Toxin Treatment
Doctors at Austin Neuromuscular Center have used botulinum toxin for more than 10 years in treating conditions such as hemifacial spasms, limb spasticity, spasmodic dysphonia, and focal dystonia. For most patients, it is a well-tolerated procedure and takes very little time to administer.
There are some patients who are not good candidates for botulinum toxin injections including those with myasthenia gravis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig’s disease,). Others who cannot receive the injections may have an allergy to the toxin.
Botulinum toxin injections can be effective and safe when they are done by a qualified neurologist. Because muscle paralysis is only temporary, the treatments are often repeated about every three months and only require a quick visit to the clinic.
Learn more about how botulinum toxin injections are used to treat certain neuromuscular disorders on the Austin Neuromuscular Center website or call us at (512) 920-0140. You may also find out more about all of the neuromuscular conditions treated at the Center here.